Chemical analysis involves determining the physical properties or chemical composition of samples.
Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES Analysis)
Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES), also known as Spark Emission Spectroscopy or Arc/Spark Spectroscopy, is a technique used for elemental analysis of solid metallic samples. It relies on the principle of exciting atoms within the sample using an electrical discharge (spark or arc), and then analyzing the light emitted by the excited atoms to determine the elemental composition of the sample.
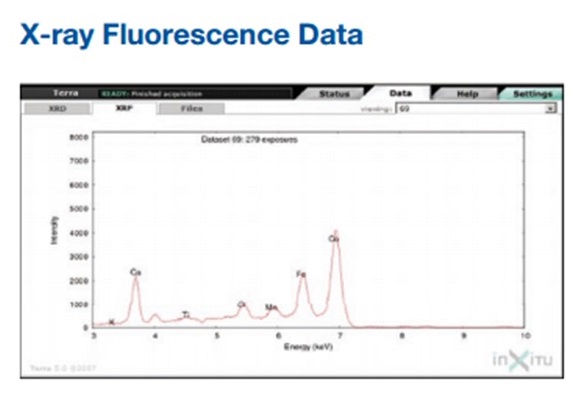
XRF Analysis
XRF (X-ray Fluorescence) Analysis is a non-destructive analytical technique used for the elemental analysis of solid, powder, and liquid samples. It relies on the principle of X-ray excitation, where atoms within the sample are excited by high-energy X-rays, leading to the emission of characteristic fluorescent X-rays. These emitted X-rays are then detected and analyzed to determine the elemental composition of the sample.
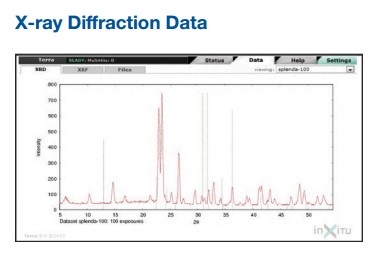
XRD Analysis
X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the crystallographic structure of materials by measuring the diffraction patterns produced when X-rays interact with a crystalline sample. XRD analysis provides valuable information about the arrangement of atoms within the crystal lattice, including crystal phases, crystal symmetry, lattice parameters, and orientation relationships.
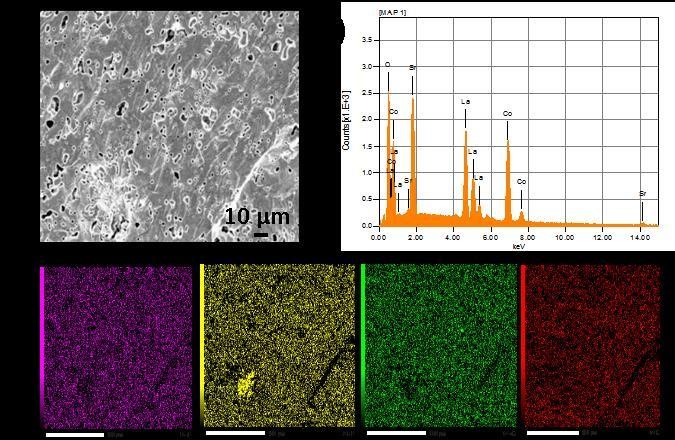
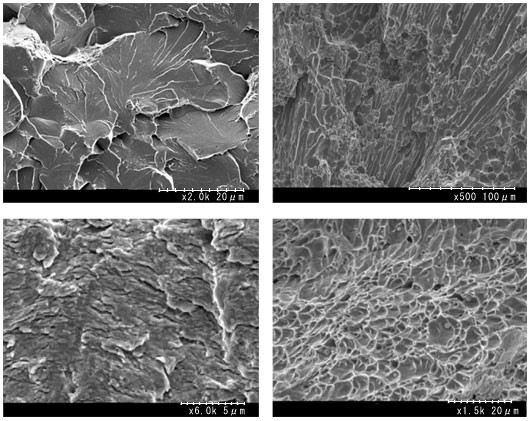
SEM Analysis
SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) Analysis is a powerful imaging technique used to obtain high-resolution images of the surface morphology and composition of materials at the micro- and nanoscale. SEM analysis provides detailed information about the topography, texture, and elemental composition of samples, making it invaluable for a wide range of scientific and industrial applications.
EDX Analysis
EDX (Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy) Analysis, also known as EDS (Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy), is a technique used to obtain qualitative and quantitative information about the elemental composition of a sample. It is often performed in conjunction with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) or transmission electron microscopy (TEM), allowing for simultaneous imaging and elemental analysis of materials at the micro-and nanoscale.